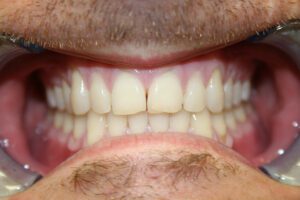
Gum or tissue grafting surgery is a painful procedure in which a gum graft is used to replace receded gum tissue. This surgery is performed to stop the process of gum recession, which if not treated on time leads to tooth loss. It also helps to minimize the effects of bone loss, which happens as a side effect of gum recession. There are two types of gum grafts: soft tissue graft and connective tissue graft. If the root has been exposed, connective tissue grafting is normally employed. Recession usually occurs as a result of extensive brushing by using a hard brush or due to severely misaligned or crooked teeth.
Recently a new treatment has been developed, which helps to restore receded gum tissue without any pain. It is known as tissue regeneration application and was developed by researchers at Tufts University School of Dental Medicine in Boston. This treatment not only reduces pain but also minimizes recovery time because it does not involve removal of sensitive tissue from the roof of the mouth. Instead, it uses platelet concentrate gel as the graft, which is applied to the collagen membrane and surgically held in place. This procedure has already been practiced on six patients, and the case study has been published in the July 2009 issue of the Journal of Periodontology.
Gingival or gum recession ultimately leads to periodontal disease if not treated on time. It is also a leading cause of tooth decay and tooth loss in adults. By using this new treatment, complete root coverage can be realized in a period of six months. People were afraid to go through gum grafting surgery because of the pain and the amount of recovery time associated with this procedure. Another advantage of tissue regeneration application is improved aesthetics, which was previously not possible with the traditional gum grafting surgery.
The graft used in this procedure has to be soaked in the patient’s blood, which is obtained on the same day. Other than this minor sting, there is no other pain involved in the procedure. So, instead of painful stitches on the roof of the mouth, the patient leaves the dental office with only a bandage on his arm. It has been found that bleeding that used to occur as a result of gum grafting was mainly due to the removal of the sensitive tissue from the roof of the mouth. Since tissue regeneration application does not involve any such procedure, there is no bleeding whatsoever after the treatment.
In order to prevent heart disease, stroke, and many other complications associated with periodontal disease, it is important to address the issue of gum recession at its early stage. With the advancement in medical science, newer and less painful procedures are now available for oral tissue grafting. Tissue regeneration application developed at Tufts University School of Dental Medicine is one of these procedures. Previously patients were afraid to have their receding gums treated because of the pain involved, but now the procedure has become very simple and straightforward. It is painless, allows less recovery time, and results in better aesthetics.